If bilateral the basilar artery is significantly smaller than normal. Move the cursor along the course of the anterior and middle cerebral artery and its branches to identify.
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy
Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery MCA The middle cerebral artery arteria cerebri media is the largest of the carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain1.

. The vertebral arteries join the basilar artery to form the vertebrobasilar system which supplies blood to the posterior portion of the circle of Willis. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery supplies the cerebellum. Superior hypophyseal artery S.
The middle cerebral artery MCA is a critical artery which has an extensive clinical significance. The MCA is part of the circle of Willis anastomotic system within the brain which forms when the anterior cerebral arteries anastomose anteriorly with each other through the anterior communicating artery and posteriorly with the two posterior communicating arteries. The basilar artery is a vital vessel contributing to the posterior cerebral circulation.
Middle cerebral artery MCA stroke describes the sudden onset of focal neurologic deficit resulting from brain infarction or ischemia in the territory supplied by the MCA. Posterior cerebral artery strokes are believed to comprise approximately 5-10 of ischemic strokes 6. Large artery occlusive lesions caused.
The middle cerebral artery MCA is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the cerebrumThe MCA arises from the internal carotid and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. The left and right MCAs rise from. This artery terminates in the pituitary portal system.
The MCA supplies most of the outer convex brain surface. It stems from the ophthalmic segment C6 supplying the infundibulum and median eminence of the. Anatomically the MCA is divided into two segments M1 and M23.
The posterior communicating artery is a location where aneurysms can potentially occur. The anterior cerebral artery anastomoses with the contralateral anterior cerebral artery via the anterior communicating artery. It is part of the circle of Willis and it branches from the internal carotid artery at the base of the brain.
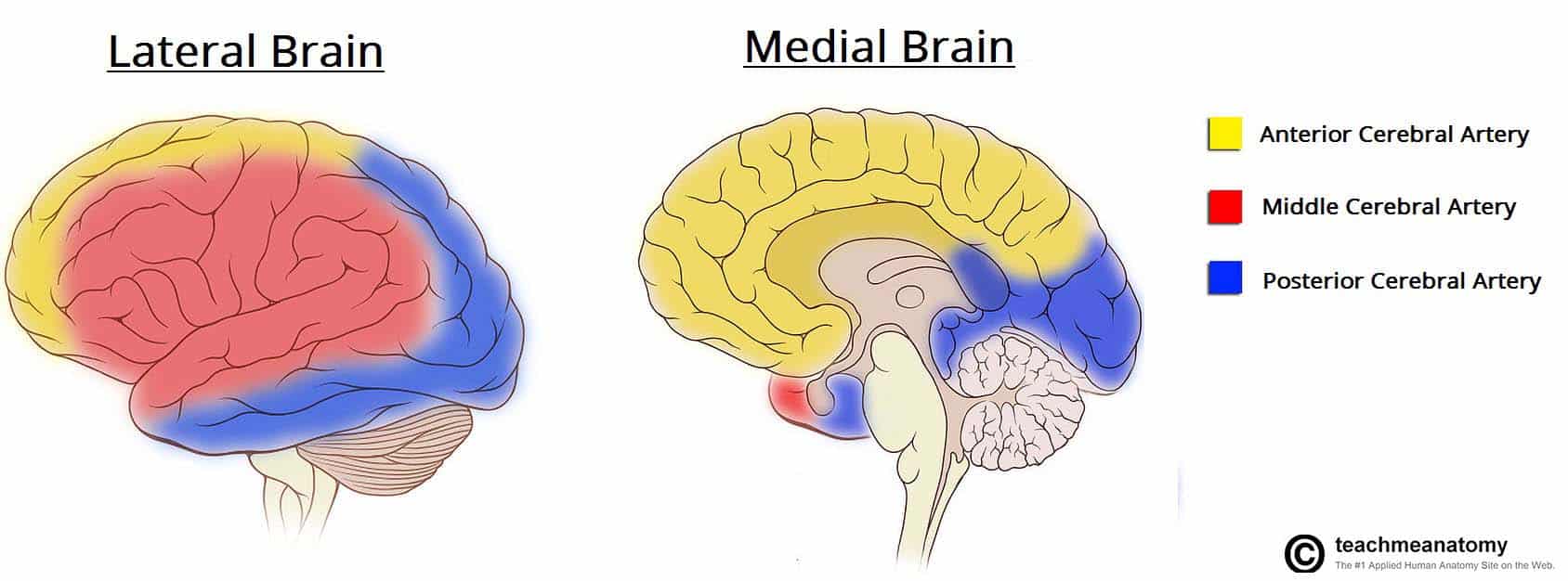
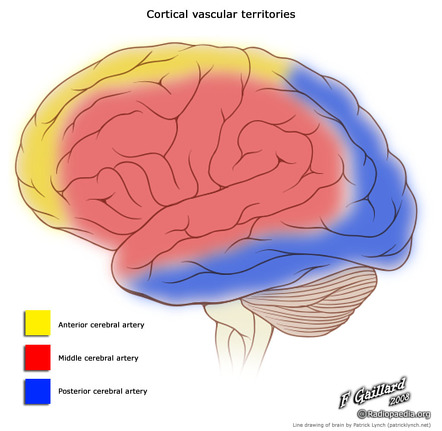
This artery also supplies blood to the primary sensory and motor areas of the face hand throat and arm2. After this the two vertebral arteries converge to form the basilar artery. The MCA is by far the largest cerebral artery and is the vessel most commonly affected by cerebrovascular accident.
The artery connects the internal carotid and the posterior cerebral arteries. A fetal origin of the posterior cerebral artery is a common variant in the posterior cerebral circulation estimated to occur in 20-30 of individuals 2. Several branches from the basilar artery originate here and go onto supply the cerebellum and pons.
An artery that supplies blood to the medial side of the cerebral hemisphere and the corpus callosum. The posterior communicating artery PCom is larger than the P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery PCA and supplies the bulk of the blood to the PCA. It is formed at the junction of the pons and medulla by the convergence of the dual vertebral arteries.
The circle of Willis is a band of arteries at the base of the brain that connects the major arterial systems to the brain. The anterior cerebral artery ACA is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brainThe two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of WillisThe left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior. Its crucial purpose is to serve the.
Perforating branches supply the posterior limb of the internal capsule part of the head and body of the caudate and globus pallidus. Of the temporal lobe anterolateral frontal lobe and parietal lobe. Its role is to provide blood supply to the brain.
Unilateral occlusion of Middle Cerebral Arteries at the stem proximal M1. Inferior hypophyseal artery I. Also coming from the cavernous segment C4 this artery supplies the neurohypophysis the posterior part of the pituitary gland.
The basilar artery terminates by bifurcating into the posterior cerebral arteries. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices. The most common causes of posterior circulation stroke are occlusion or embolism from large artery vertebrobasilar atherosclerosis or dissection and embolism from the heart11 12 In a large US hospital registry study of 407 patients with posterior circulation stroke embolism was the most common mechanism 40 of patients.
Symptoms of posterior cerebral artery stroke include contralateral homonymous hemianopia due to occipital infarction hemisensory loss due to thalamic infarction and hemi-body pain usually burning in nature. Anterior cerebral artery Arteria cerebralis anterior The anterior cerebral artery is the terminal branch of the communicating segment C7 of the internal carotid arteryBeing located in the anterior and medial aspects of the interhemispheric fissure the anterior cerebral artery supplies a large portion of the medial cerebral hemispheric surfaces namely the corpus. Arterial Circle of.

Posterior Cerebral Artery Wikipedia

The Posterior Cerebral Arteries Youtube
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13349/KlvAXLEbE4kwyNXlloc8bA_A._cerebri_posterior_01.png)
Posterior Cerebral Artery Anatomy Branches Supply Kenhub
Posterior Cerebral Artery Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Posterior Cerebral Artery Neuroangio Org

Posterior Cerebral Artery Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
0 comments
Post a Comment